

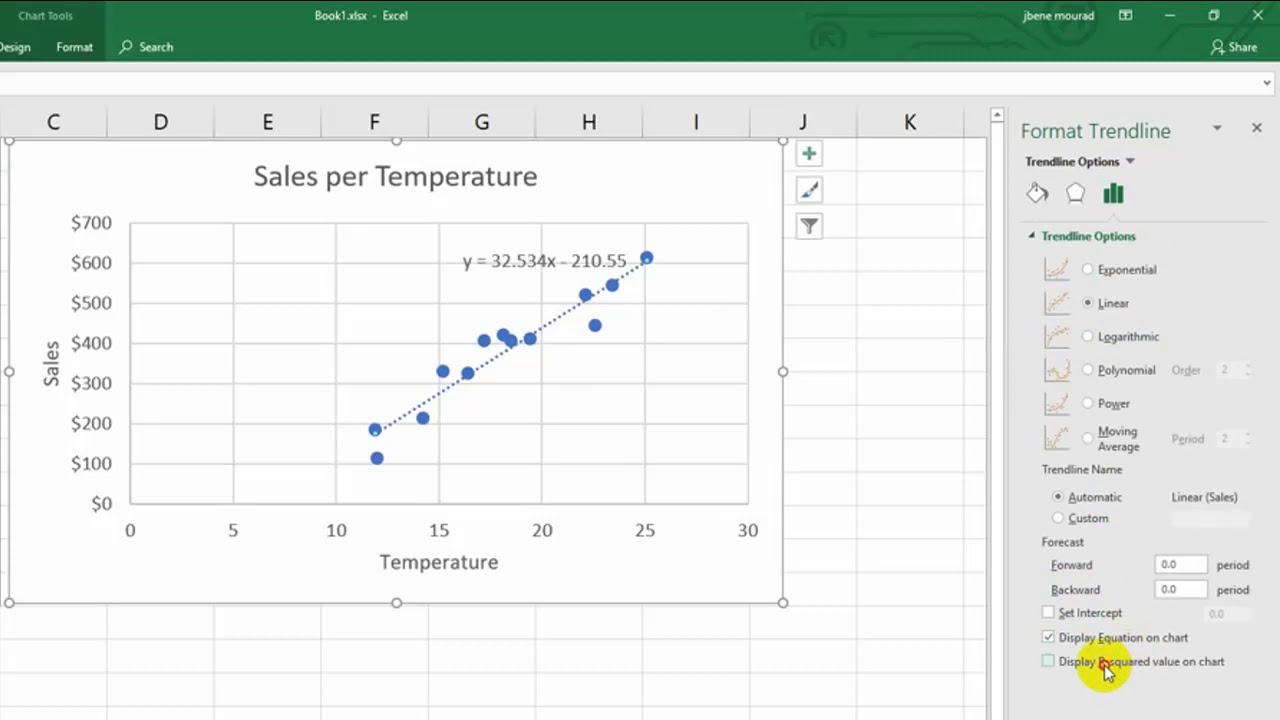
Let’s talk about each element of the table a bit more in detail: Notice how the helper table starts with a dummy row ( E2:H2)-this determines the reference angle. Set up a separate dummy table as follows: To build the plot, you need to compute the polar coordinates first and, once there, convert them to the x- and y-axis values used by Excel to create the chart. Right off the bat, outline a helper table where all the calculations for your chart will take place. Since CSAT scores are commonly expressed as a percentage scale, consider the following table:
For the record, this article is based on the tutorial created by Jon Peltier.
In this in-depth, step-by-step tutorial, you will learn how to turn your raw data into a polar plot in Excel from the ground up. Also, don’t forget to check out the Chart Creator Add-In, a powerful tool for building mind-blowing advanced Excel charts and graphs in just a few clicks. The plot enables you to quickly assess the good and bad months for each company, which facilitates better decision making.Įxcel doesn’t support this chart type-in fact, it can’t even read polar coordinates-meaning you will have to build it from scratch. The polar plot comes in handy when the analyzed data has a cyclical nature.Īs an example, the chart below compares the customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), a metric that illustrates a customer’s satisfaction with a brand or product, of two organizations throughout 2019: Simpson Ltd and Griffin Ltd. The plane itself is made up of concentric circles expanding outward from the origin, or the pole-hence the name. Theta (θ) – The angle from a reference angle.Radius ( r) – The distance from the center of the plot.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
